microscopic examination of sperm count is very important for the study of morphology of sperm and motility of sperm and also normal range(15 million to 200 million/millimeter) of sperm count is defined by this process.
Defined topic name in this page
- Motility of a sperm
- Determination of sperm count(range)
- Calculation
- Morphological examination of spermatozoa
To check motility of sperm by microscopic examination of sperm count
- To check the motility of sperm place a small drop of liquefied semen on the glass slide and cover it with a Cover slip.
- Examine the cover sleep preparation under the high-power objective lens.
There are 4 classifications of motility of sperm
- Rapid progressive motility:- active
- Slow progressive Motility:– Sperm may be less linear in their progression.
- Non-progressive Motility;– sperm is described as shaking.
- Immortality:- sperm don’t move
.Determination of sperm count(range)
- This is a measurement of how many millions of sperm are there in each ml of fluid.
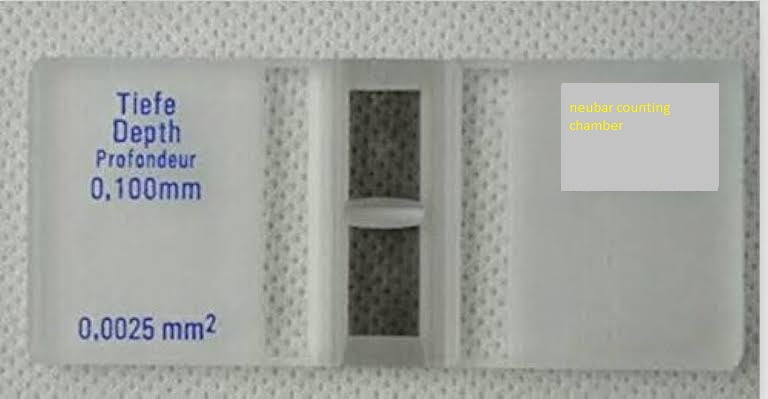
- The number of sperm count in the sample can be estimated in a counting chamber after diluting the sample.
- Draw diluted semen to the 0.5 mark of a WBC pipette and draw cement diluting fluid to the 11 mark and mix well.
- Charge the number chamber and allow the sperm to settle wait 5 minutes.
- microscopic examination of sperm Count in the four corner squares of neubar chamber
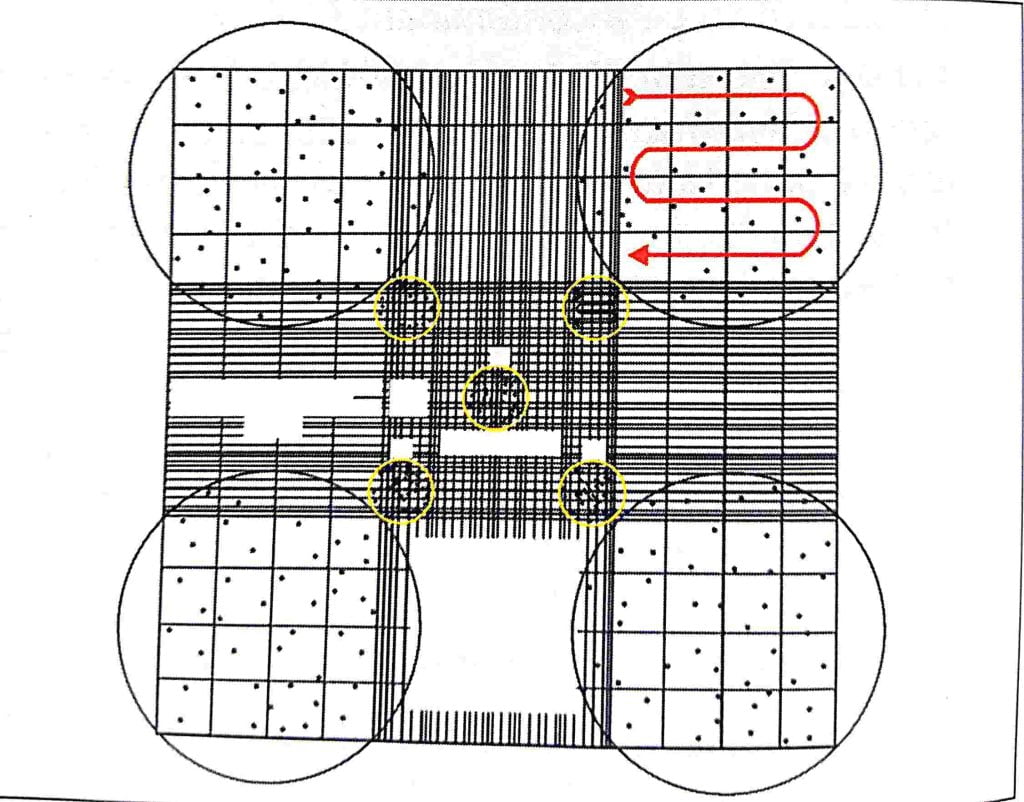
Calculation:-
count x 10 x 20 x 1000 / 4
Morphological examination of spermatozoa
- For morphological examination of semen thin and uniform smear is prepared on a clean grease-free slide.
- And dried in the air and its fixed by heat by moving the slide over the flame 2 to 3 times.
- Then 1% chloramines is added and kept few minutes to remove excess mucus.
- Staining should be done as described below:-
- Flood the smear with Ziehl Nielsen stain and keep for 1 to 2 minutes.
- Then wash with water.
- Counter Stain with loffelers methylene blue and keep for half to one minute.
- Wash with Water.
- Dry and examine under the oil immersion Lens of the Microscope
Result:-
Head of spermatozoa:- purple color
Tail and middle piece: – red or pink color depending on duration of Staining.
Examine 100 to 500 spermatozoa and observe for the following
- Heads – too large or too small, pointed, ragged, edges, atypical distribution of chromatin presence of acetophyll, vacuoles double head constricted Head, acute taping, head hi any, head immature is spermatozoa and amorphous form of spermatozoa.
- Middle piece: – absent swollen bifurcated
- Tail:- double curled, bifurcated, rudimentary or absent.
- Finally, the smear is also examined for the presence of pus cells, RBCs, macrophages, epithelial cells testicular cells and Crystals. Abundant Crystals may be found in the smear especially when kept a semen for some time.
- semen containing about 20% a normal spermatozoa is still considered fertile.
- microscopic examination of sperm count is done
Table of Contents
What is a normal sperm count?
normal sperm count is 15 million to greater than 200 million sperm per milliliter of semen.
What is a good sperm count to get pregnant?
god sperm count for the pregnant is more than 15 million per millimeter AND it is check by lab test o microscopic examination of sperm count
What is the microscopic examination of sperm?
microscopic examination of sperm count is done to check the normal range and morphology of sperm.

