RBC COUNT 1.Red blood cell count:-
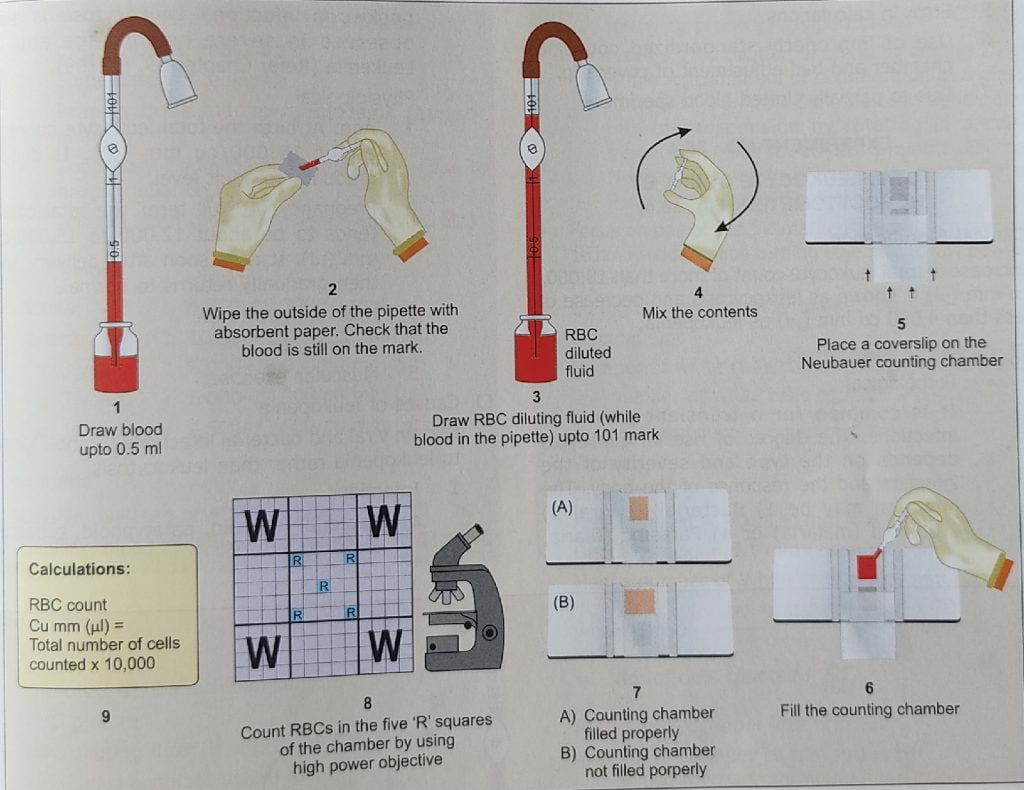
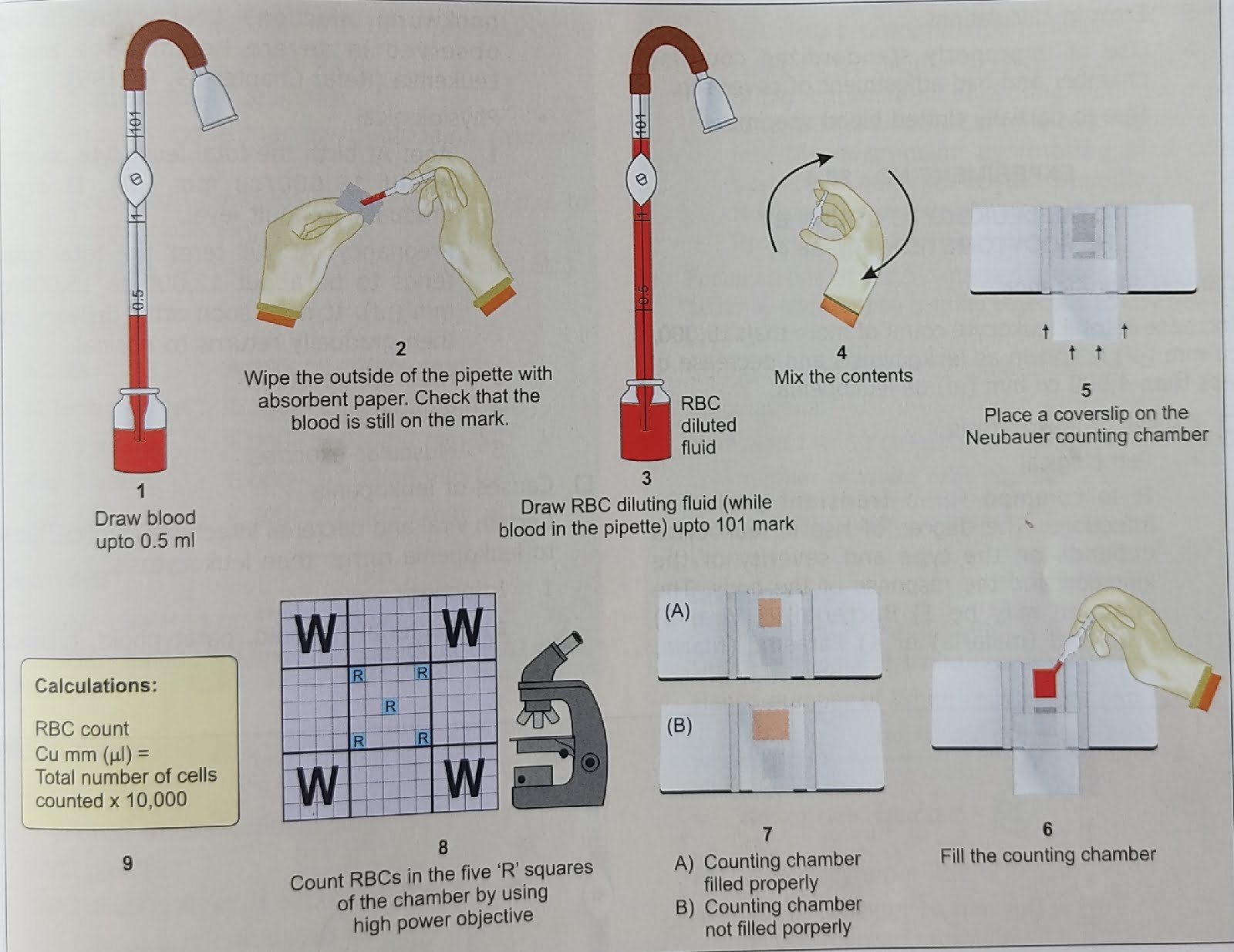
Stages of RBC count estimation by haemocytometer.
1. Introduction
2.principle
3.Requirement
4.method
5.procedure
6.clinical significance
1.INTRODUCTION RED BLOOD CELL COUNT
:-Red blood cell count is the important for the diagnosis of haemotological test and it is very important to the calculate the MCV
and MCH
:- the manual method of RBC count is the time consuming .
2.PRINCIPLE OF RED BLOOD CELL COUNT
:- The blood specimen is diluted 200 times with the RBC diluting fluid and cell are counted high power of microscope by the help of neubar counting chamber.
3.Requirement
:-microscope
:-neubauer chamber
:- RBC diluting fluid
:- RBC pipette
:- collection apparatus
Syringe 💉
Cotton
Tourniquate
Spirit
Preparation of RBC diluting fluid
:- sodium citrate :3.0 gram
:- formalin. : 1.0ml
:-distilled water : 100ml
Note :- this solution is stable at room temperature 🌡️ (25°c) for at least one year
Specimen
:-Double oxalate or EDTA blood.
:- capillary blood.
4.methoad
1.capillary method
2. Tube method
1.capillary method
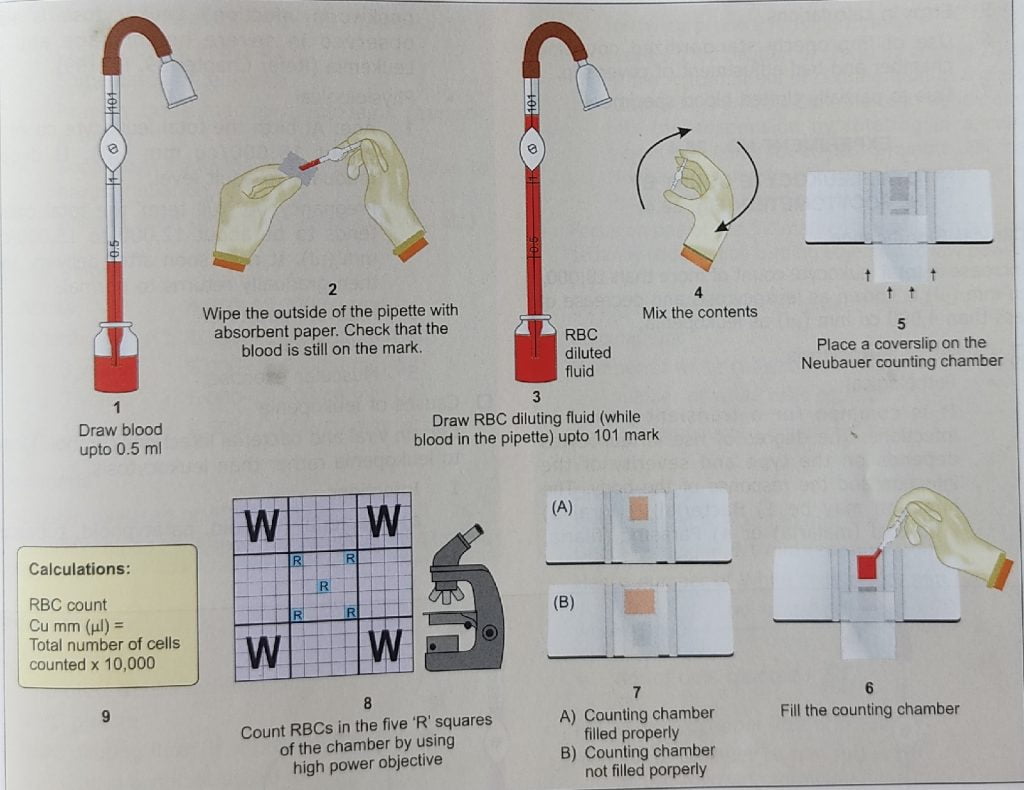
5.procdure.
A :- draw the blood up to 0.5 mark in RBC pipette.
B :-carefully wipe the access blood out side the pipette with dry cotton or tissue paper.
C:-draw the RBC diluting fluid up to 101 mark.
D :- mix it properly and wait for 3_5 minute.
E:-discard few drop of diluted blood .
F:-cover slip is placed centrally on neubar counting chamber.
G:- A drop of diluted blood is obtain at top of the pipette and touch the junction of neubar and cover slip and charged the neubar .
H .After charge wait 3 to 5 minute to the settle down of RBC .
I.after waiting ready to the count by Microscope 🥰
Normal range
In male :- 4.5 to 5.5 million cells/ cu mm
Method :-2
Tube method
All procedure Same only specimen and diluting fluid change .
Specimen:- 20 microliter or .002 ml
Diluting fluid :- 3980 microliter or 3.98 ml
PRINCIPLE OF RBC COUNT?
The blood specimen is diluted 200 times with the RBC diluting fluid and cell are counted high power of microscope by the help of neubar counting chamber.