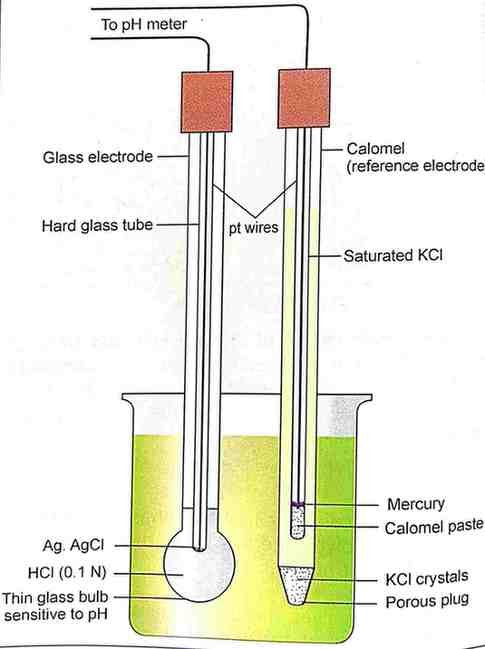
Amperometry in chemistry is the detection of ions in a solution based on electric current or changes in electric current.
Table of Contents
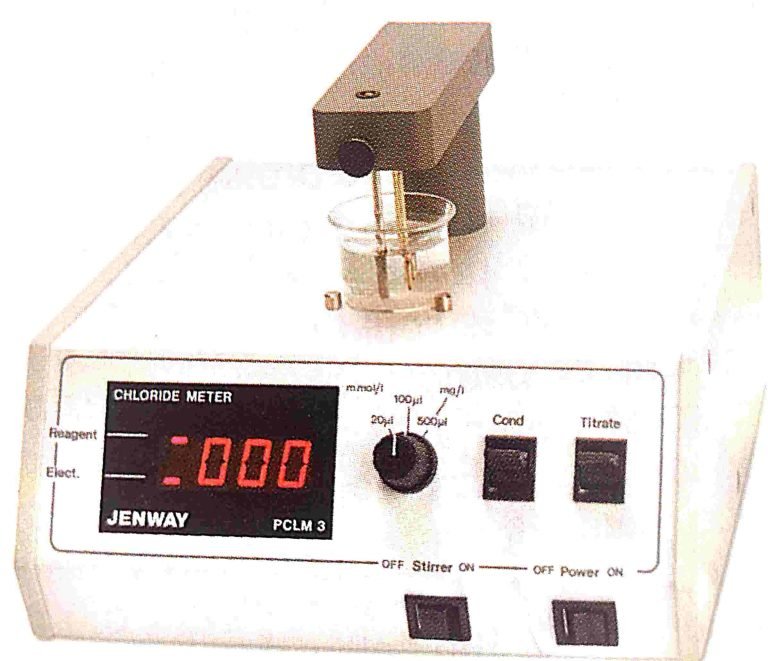
Introduction of amperometry:-
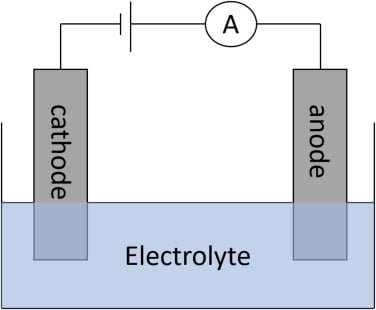
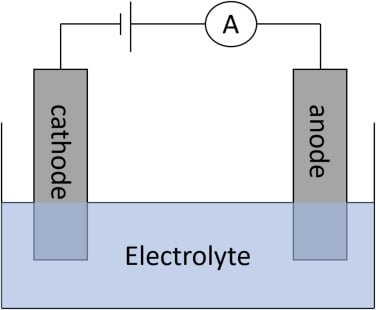
This technique is based on the measurement of the current flowing through an electrochemical cell when a constant potential is applied to the electrodes.
Example: PO2, electrode.
- The po2 electrode is a complete electrochemical cell consisting of a small platinum cathode a Silver/ Silver chloride anode and potassium chloride in phosphate buffer.
- Then platinum cathode is covered by a thin film of electrolyte.
- It is separated from the test solution by a polypropylene membrane, which is permeable to gas.
- When no oxygen is present in the test solution the cathode is polarized and the current is almost zero.
- When the PO2, electrode is dipped in a test solution, in the presence of oxygen in the sample a current develops due to the diffusion of oxygen from the test solution through the membrane to the cathodes where it gets reduced.
- The current is directly proportional to PO2, in the test solution (Blood)
What is the basic principle of amperometry?
it involves the measurements of currents at constant voltage applied at the dropping mercury electrode.
What do you mean by amperometr?
it is in chemistry is the detection of ions in a solution based on electric current or changes in electric current.