- Method of total protein test
- Introduction of total protein test
- Principle of total protein test
- Reaction of total protein test
- Sample
- Procedure
- Calculation
- Clinical significance
Method of total protein test
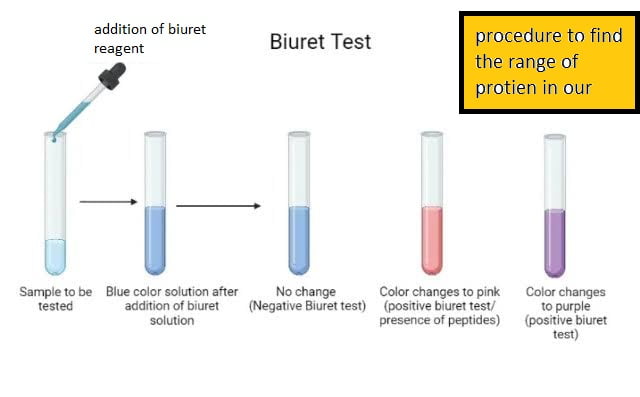
Total protein determination by BIURET TEST METHOD .
Introduction of total protein test ( biuret test)
- Proteins are the most abundantly distributed organic compound.
- They are large molecules consisting of amino acids which our body and cell in our body need to function properly.
- Our muscles skin bones and many parts of anybody contain a significant amount of protein.
- Protein counts for 20% of total body weight.
- Proteins are large to be observed by the intestine and must be hydrolyzed to yield amino acids which can be observed Proteins are not stored in the human body they are consistently broken down in their constitute amino acid and then reused in Protein synthesis.
- Proteolytic enzymes are responsible for degrading protein and are produced by three different organs that is stomach pancreas a small intestine.
Principle of total protein test
Protein in an alkaline medium binds with the cupric Ion present in the Biuret test reagent to form a blue-violet color Complex the intensity of the color formed is directly proportional to the amount of protein present in the Sample.
Reaction of total protein test
Total protein + cu++ = Blue-voilet color complex
Sample
Serum / EDTA / Plasma
Procedure
| Blank | standard | Test | |
| Biuret reagent (ml) | 1 ml | 1 ml | 1 ml |
| distilled water | 0.01 ml | – | – |
| standard | – | 0.01 ml | – |
| sample | – | – | 0.01 ml |
- First of all take three glass tubes and mark 1. Blank 2. standard 3. test.
- Add one ml biuret reagent in each tube.
- Add Distilled water 10 microlitres in a blank test tube.
- Add standard 10 microlitres in standard test tubes.
- Add sample 10 microlitre in the test test tube.
- Mixed well and incubate for 5 minutes at room temperature.
- Measure the optical density of a standard and test against a blank with a yellow-green filter of 550nm on a Colorimeter.
Calculation
total protein:- OD OF TEST /OD OF STANDARD X CONCENTRATION OF STANDARD
Clinical significance
Through osmotic pressure, protein is involved in the maintenance of normal distribution of water between blood and Tissue.
Several fractions of serum protein are very independent and widely in disease.
Hypoproteinemia
- Low level of protein less than 6 grams/dl
- Hypoproteinemia loss of protein through skin burns.
- Loss of protein through urine nephrotic syndrome kidney disease
- Malabsorption
- Decreases synthesis of protein
Hyperproteinemia
- A level of protein of more than 8 grams in body l indicates hypertropia in the case of
- Multiply myeloma
- Dehydration
- Chronic diseases
What is the principle of biuret method?
Protein in an alkaline medium binds with the cupric Ion present in the Biuret test reagent to form a blue-violet color Complex the intensity of the color formed is directly proportional to the amount of protein present in the Sample.
What colour is the biuret test?
blue liquid that changes to purple color
Why is the biuret test blue?
Protein in an alkaline medium binds with the cupric Ion present in the Biuret test reagent to form a blue-violet color