Bleeding time is a clinical laboratory test performed to evaluate platelet function.
- Introduction
- Principle
- Method
- Specimen
- Normal Range
- Requirement
- Procedure
- Note
Introduction
- Determination of bleeding time helps to detect vascular defects and platelet disorders.
- Prolonged bleeding time is generally associated with thrombocytopenia. In the case of von Willebrand’s disease, bleeding time is high with a normal platelet count.
- It is caused by a platelet defect combined with factor VIII deficiency.
Principle of bleeding time
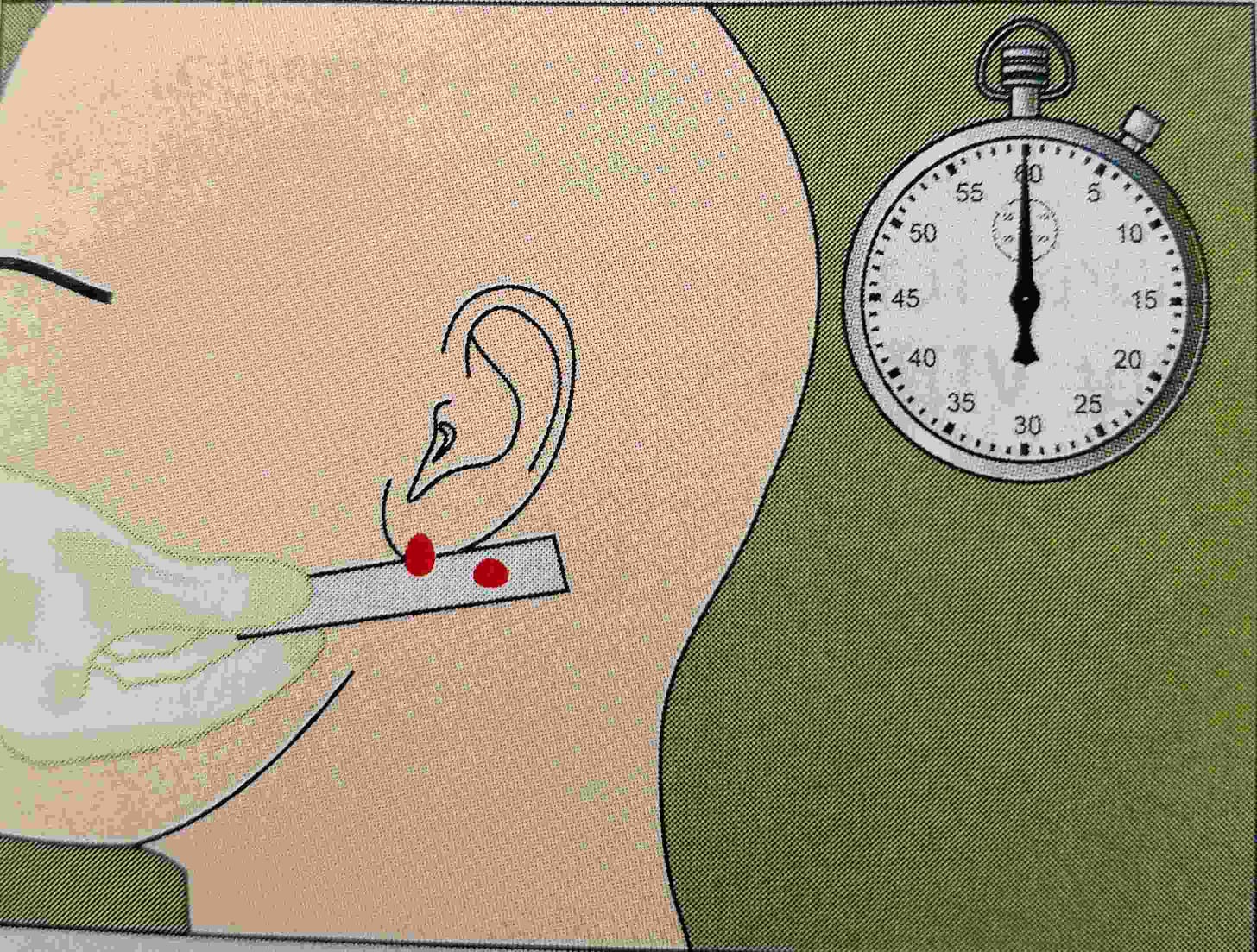
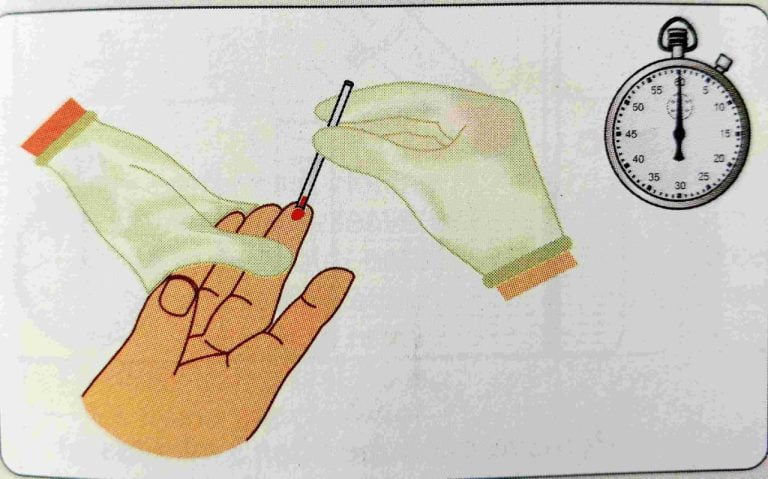
- 1Mm deep puncher is made on The ear lobe or finger of a patient. The length of time required for bleeding to cease is recorded.
Table of Contents
Method
Dukes method
Specimen
Blood Collected by ear lobe or fingertip.
Normal Range
1 to 5 minute
Requirement
- Sterile lancet
- Spirit or 70% alcohol
- Circular filter Paper
- Stopwatch
Procedure
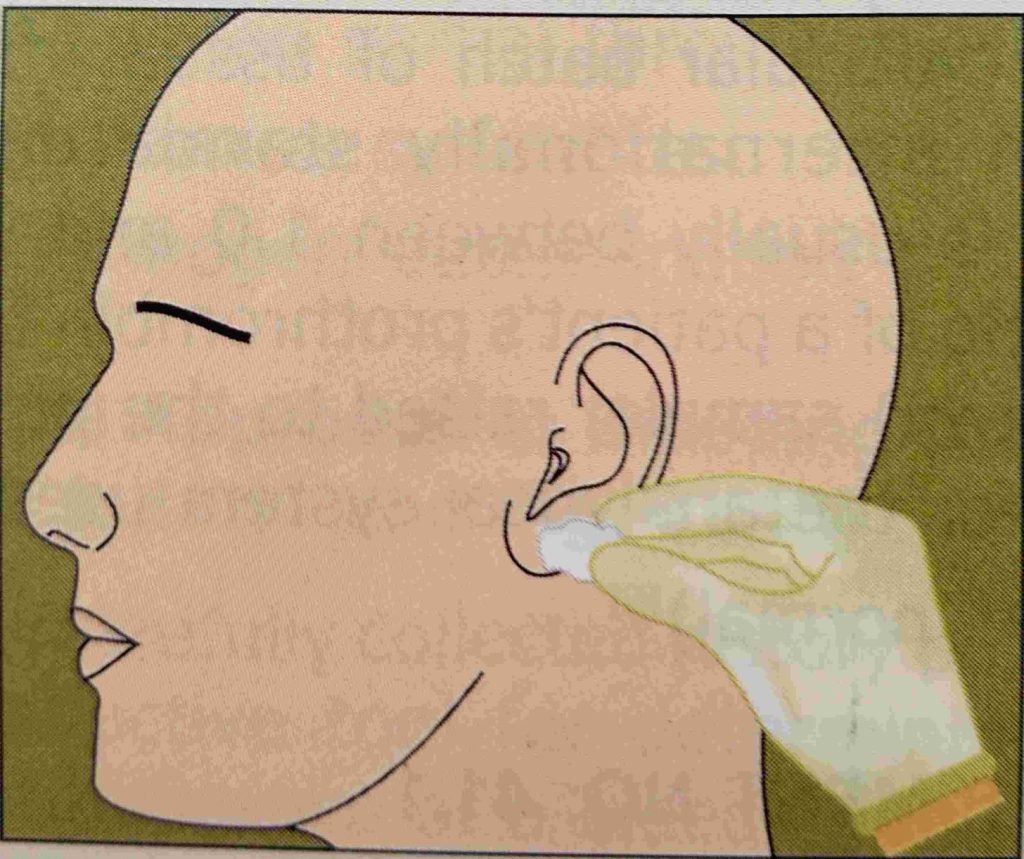
clean the fingertip and earlobe of the patient with a cotton swab
- Prick the ear lobe (fingertip) with a disposable and sterile needle or lancet deep up to 3 mm.
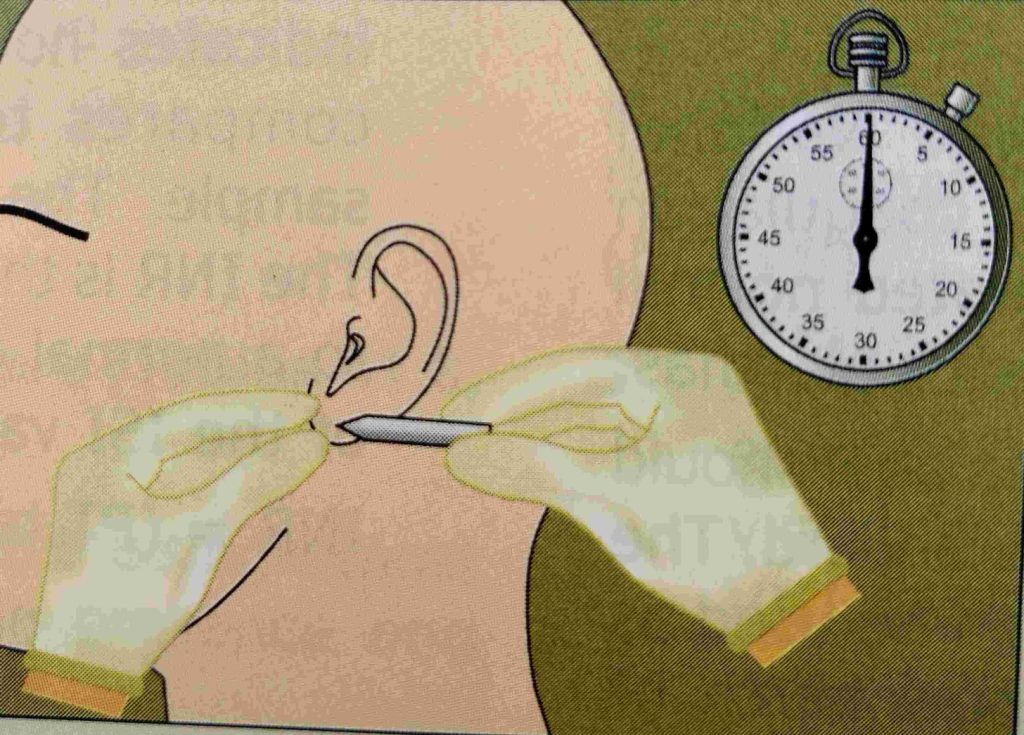
- Start the stopwatch the blood should flow freely without squeezing the earlobe (or fingertip).
- After 30 seconds collect the drop of blood at one corner of the filter paper do not touch the skin with the paper.
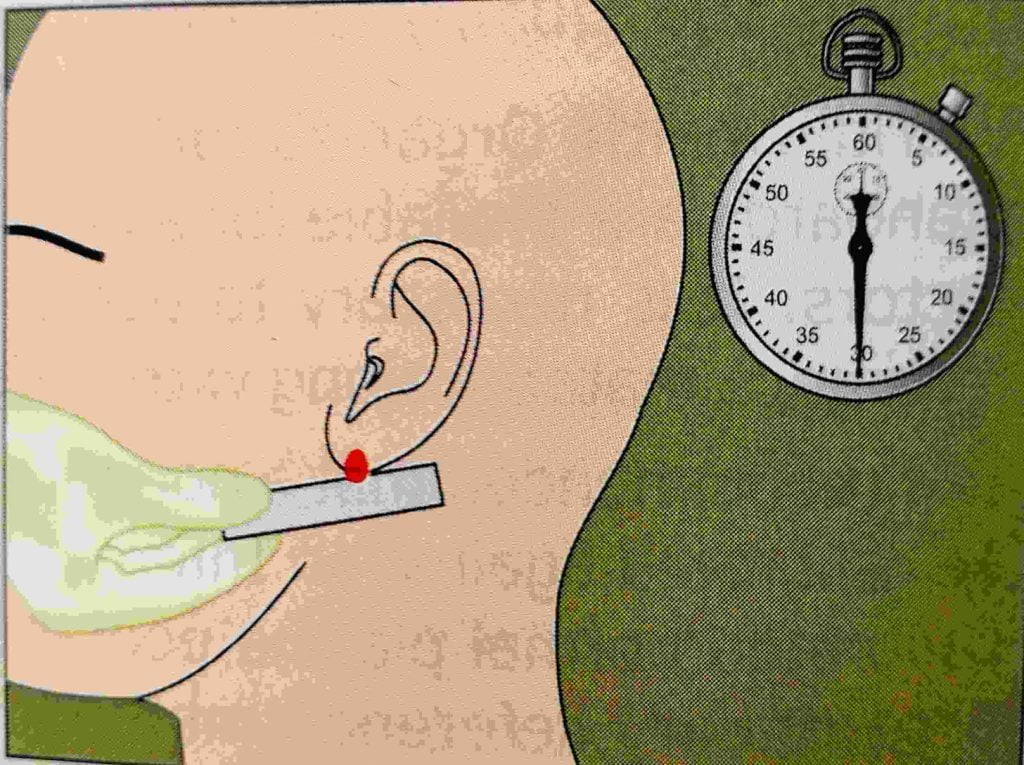
- It repeated three times in between the duration of 30 seconds.

- When bleeding is stopped then stop the time and note down the time.
NOTE :- if the bleeding is Prolonged for more than 10 minutes discontinue the test apply pressure to the bleeding stop
What is a normal bleeding time?
normal BT is 1 to 5 minute.
What is normal BT and CT time?
normal BT is 1 to 5 minute and normal clotting time is 4 to 9 minute.
How to calculate bleeding time?
The time from the beginning of incision until the termination of bleeding is considered as the BT