Electrophoresis:-
- Introduction
- Principle
- Requirement
- Procedure
- Types
1. Electrophoresis: –
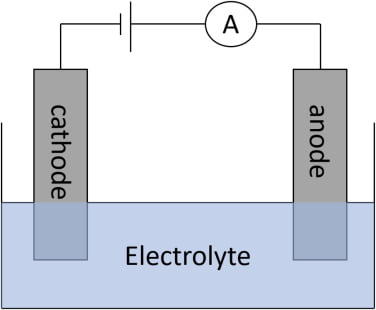
The term electrophoresis describes the migration of change particles under the influence of an electric field.
2. Principle: –
Many important biological molecules such as amino acids, peptides, proteonucleotides and nucleic acid at a given pH exist in solution as electrically charged species either ions or cations under the influence of an electric field the charge particle cation migrates to the cathode ( negative electrodes) or anion moves to the anode (positive electrode ) depending on the nature of their net Charge.
3. Requirement: –
- Power supplier
- Buffer tank with electrode
- Buffer
- Fixative
- Staining solution
- Destaining solution
- Densitometer
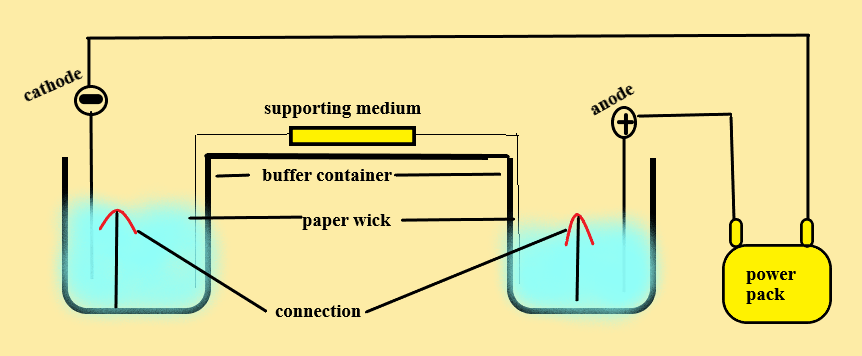
Method or procedure: –
- Equal quantities of buffer are placed in the cathode and anode compartments.
- The sample is layered on the supporting medium.
- The supporting medium is connected to the buffer by a paper wick.
- Electrical current is passed by means power pack with fixed voltage.
- After the electrophoretic run, the supporting medium is placed in a fixative for 10 minutes.
- Staining of the supporting medium is performed for a specific period.
- Destaining of the supporting medium is Performed.
- The stained supporting medium is placed in a fixative 10-minute.
- After dried The Staind supporting medium is scanned by using a densitometer.
Densitometer:-
A Densitometer is essentially a double-beam filter photometer or spectrophotometer that scans the electrophoretic strip in the form of agarose cellulose as it moves past the optical system.
Types:-
Two types of techniques to form Electrophoresis.
- Blot technique
- Southern and Northern blot technique