- Introduction of glucose tolerance test
- Etiology and epidermiology
- patient preparation for glucose tolerance test
- Procedure
- Result
- Graph
- Factors affecting glucose tolerance test
- Clinical significance
Introduction of glucose tolerance test:-
- Glucose tolerance means the ability of the body to utilize glucose in blood circulation. Glucose tolerance decreases in diabetes mellitus & certain endocrine disorders like hyperthyroidism, hyperpituitarism & hypoadrenalism.
- Blood sugar in the case of a normal individual remains fairly constant throughout the day, about 1 mg/ml. Following food intake, there is a temporary rise in blood sugar, the extent and duration of which depends on the type of food taken. Blood sugar levels return to normal within two to three hours after taking food. In decreased glucose tolerance, however, blood glucose level does not return to normal within 2 to 3 hrs after food intake. This effect of ingested carbohydrates can be studied under reasonably standard conditions using the glucose tolerance test.
- A glucose tolerance test can be used to diagnose type 1 Diabetes mellitus type 2 Diabetes mellitus and Gestational diabetes (diabetes during Pregnancy).
Etiology and epidermiology:-
- Diabetes mellitus is a condition of hyperglycemia.
- In Type 1 Diabetes mellitus antibodies are triggered in an autoimmune reaction leading to the destruction of the Bita cell in the pancreas.
- The pancreas fails to produce a sufficient amount of insulin to bind the glucose since there is little available insulin the blood sugar Increases.
- In type 2 Diabetes mellitus the cells in the liver become insulin resistant causing reduced absorption of glucose in the bloodstream often the pancreas produces insulin in response to the increased amount of glucose in the bloodstream but with the liver’s inability to absorb the glucose, the result is hyperglycemia.
- Gestational Diabetes mellitus is also a diabetes of insulin resistance sign of gestational diabetes usually appears around the second trimester of pregnancy and it resolves upon compilation of pregnancy all gestational diabetes is resolved for some it carries are risk for developing type 2 Diabetes.
patient preparation for glucose tolerance test:-
- The patient should have been taking carbohydrate-rich diet for at least 3 days before the test.
- All the drugs that influence carbohydrate metabolism should be De continued for at least 2 days.
- The patients should avoid strenuous exercise on the previous day of the test.
- He and she should be an overnight at least 10-hour fasting Stage.
- During the test, the patient should refrain from smoking and exercising.
Procedure:-
- A glucose tolerance test should be conducted in the morning.
- A fasting blood simple is drawn and urine collected.
- The patient is given 75 grams of oral glucose dissolved in 300 ml of water to drink within 5 minutes.
- Blood and urine simply circulated at 30-minute intervals for at least 2 hours.
- All the symbols are subjected to Estimation and urine samples are qualitative tests for glucose.
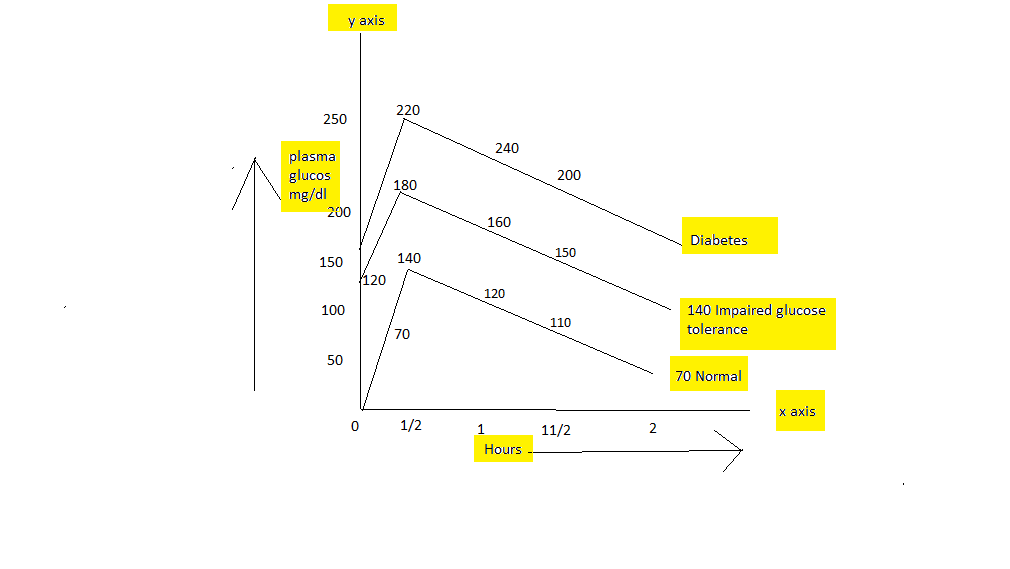
- Prepare a glucose tolerance curve by plotting time on the x-axis and plasma glucose value on the y-axis.
Result:-
| Normal result | Impaired | Abnormal |
| fasting 60-110 | 100-125 | greater than 126 mg/dl |
| one hour- less than 200 | Two hour after | After two hour |
| two hour- less than 140 | 140-200 mg/dl | Greater than 200 mg/dl |
Graph:-

- Patient with impaired glucose tolerance slowly developed frank diameter (pre-diabetes)at on estimated rate of 2% per year.
- Dietary restriction and exercise are recommended for the treatment of impaired glucose tolerance.
Factors affecting glucose tolerance test:-
- Starvation injection of high fat diet.
- exercise.
- Pregnancy- tolerance is decreased
- Illness
- Physiological decrease tolerance with age
- Endocrine disorders
- drugs
- liver disease
Clinical significance:-
- The glucose tolerance test is given to determine how quickly glucose is cleared from the blood the test is used to test for diabetes insulin resistance impaired beta beta cell functions reactive hypoglycemia acromegaly and other disorders of carbohydrate metabolism.
What is in a glucose tolerance test?
The patient is given 75 grams of oral glucose dissolved in 300 ml of water to drink within 5 minutes.
Blood and urine simply circulated at 30-minute intervals for at least 2 hours.
All the symbols are subjected to Estimation and urine samples are qualitative tests for glucose.
What is a normal glucose tolerance level?
normal and abnormal given in the graph