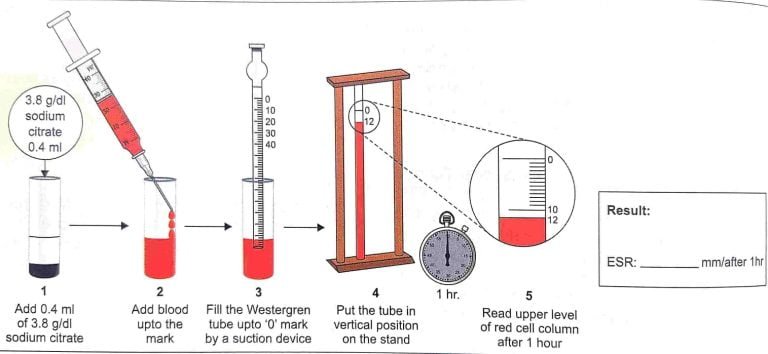
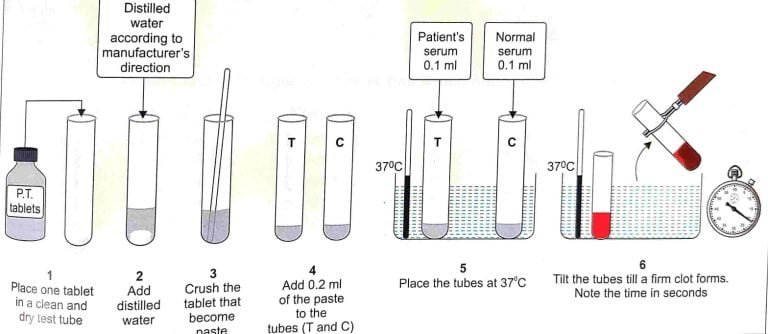
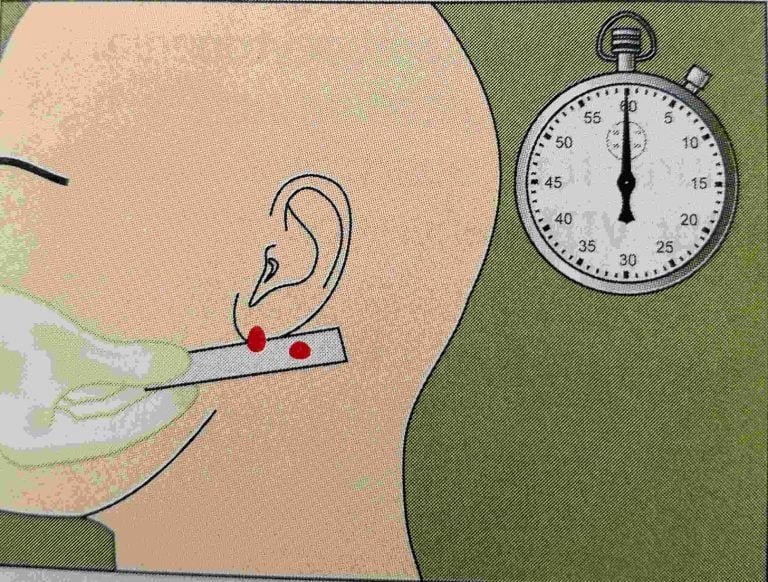
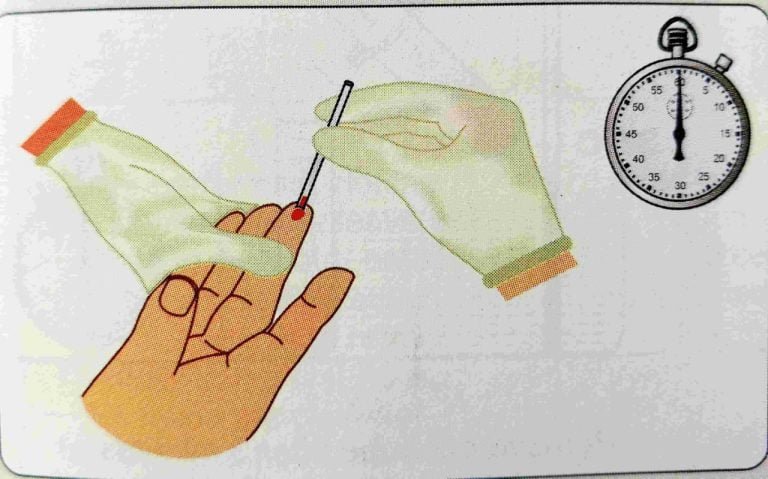
- Introduction
- Normal range
- Principle
- Requirements
- Procedure
- Clinical Significance
Table of Contents
Introduction of reticulocyte count
Reticulocytes are slightly immature red blood cells. A reticulocyte count is a blood test that measures the amount of these cells in the blood.
Normal range of reticulocyte count
Adults: 0.2 to 2%
Infants: 2 to 6%
Principle of reticulocyte count
Supervital staining method is used for reticulocyte count. Blood is mixed with the stain and the stain enters the cells in living condition. The RNA in the cells is precipitated by staining as dark blue network or reticulum. Blood smear is made afterwards. Since a direct count is not possible, a relative count is taken against the number of red blood cells and expressed as a percentage of red cells.
Requirements
- Grease free glass slides
- Test tube (15 x 125 mm)
- Pasteur pipette with rubber teats
- Capillary tube
- Test tube rack
- Microscope
- Reagent
Reagent
Staining solution: It is prepared as follows:
- a) Brilliant cresyl blue: 1.0 g
- b) Sodium citrate : 0.4 g
- c) Sodium chloride : 0.85 g
- d) Distilled water to : 100 ml.
Dissolve first sodium citrate in normal saline and then the dye. Filter it and store in a plastic container. It is stable at 2-8°C.
sample/ specimen
EDTA anticoagulated or capillary heparinized blood. The specimen need not be a fasting sample. Perform the test within 2 to 3 hours of blood collection.
Procedure
- Filter a small amount of the stain (about 5 ml).
- In a test tube add two drops of blood and two drops of the stain (by using two separate Pasteur pipettes). Mix thoroughly.
- Cover the tubes with cotton plug and keep at 37°C for 30 minutes.
- Prepare a thin smear of the stained blood specimen by using a spreader slide. Air dry the smear.
- First examine the smear under the low power objective and locate a portion of the smear, where the red cells are evenly distributed,
- Change to the oil immersion objective. Reticulocytes are identified by fine, deep violet filaments and granules arranged in a network. Red cells stain pale blue. Simultaneously count reticulocytes and red cells in about 15 fields.
calculation
Number of reticulocytes counted × 100 Number of red cell
Clinical Significance
The number of reticulocytes in peripheral blood is a reflection of red cell forming activity (erythropoietic activity) of bone marrow. Increase in their number indicates increased activity of the marrow (hemolytic anemia or acute blood loss). This is known as reticulocytosis. Repeated absence or low counts of reticulocytes indicate bone marrow suppression (aplastic anemia).