Synopsis

Introduction of bone
- Etymology
- Definition
- Properties
- Function
- Classification
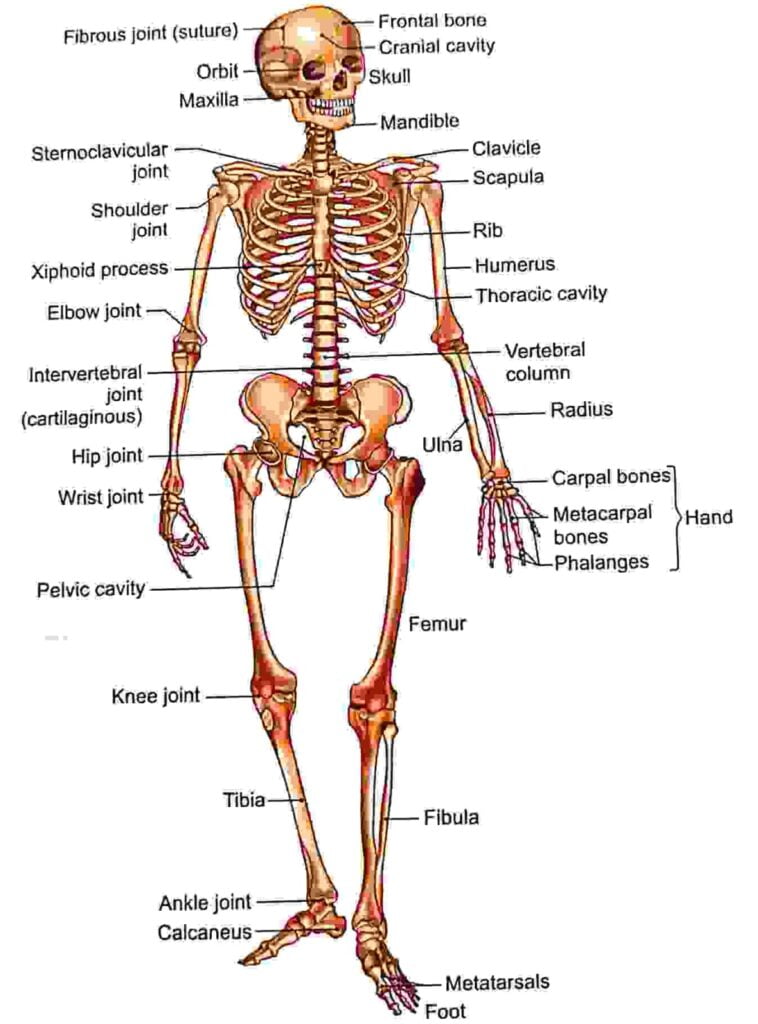
- Picture
Etymology
- Bone
- Derived word = anglo-saxon
- Meaning=bar
Definition [ introduction of bone]
- Bone is a hard part of the body that provide dynamic structure frame to the body.
- The study of is called osteology .[ Osteo= bone, logy=study]
Properties
- Bone is living tissue
- Bone is supplied by arteries and nerves
- Bone is drained by veins
- Bone grows with age
- Bone is subject to disease
- Bone regenerates when damaged
- Fracture bone heals leading to union
- Bone can undergo remodeling
- Bone can withstand strains and stresses
- Bone can atrophy or hypertrophy
Function
- Bone provide frame work to the body
- Bones accord shape to the body
- Bone is site of blood formation
- Bone is store house of calcium and phosphorus
- Bone provide protection to the number of viscera
Classification
- There are three classification of bone.
- 1. Morphological classification
- 2. Regional classification
- 3. sesamoid bone
Morphological classification
- On the basis of shape:- it is of six type
| 1. Long bone | Femur , Humerus |
| 2. Short bones | carpal , tarsal |
| 3. Short long bone | Metacarpal, metatarsal |
| 4. Flat bone | Parietal , scapula |
| 5. Irregular bone | Hip bone , vertebra |
| 6. Pneumatic bone | Maxilla , sphenoid |
morphological classificationRegional classification
- On the basis of region it is two type
- 1. axial bone = it include 80 bones
- 2. Appendicular bone = it include 126 bone
| Axial bone = 80 bone | Appendicular bone = 126 bone |
| I. Skull bone = 28 | I. Upper limb = 64 |
| II. Vertebra bone = 26 | II. Lower limb = 62 |
| III. Ribs = 24 | |
Iv. Sternum = 01
v. Hyoid bone = 01 | |
Regional classificationSesamoid bone
- It is special type of bone that ossify after birth.
- It is develop in the tendon of a muscle.
| Sesamoid Bone | Tendon of muscles |
| I. Patella | Quadriceps |
| II. Pisiform | Flexor carpi ulnaris |
| III. Fabella | Lateral head of gastrocnemius |
| IV. Rider’s bone | Adductor longus |
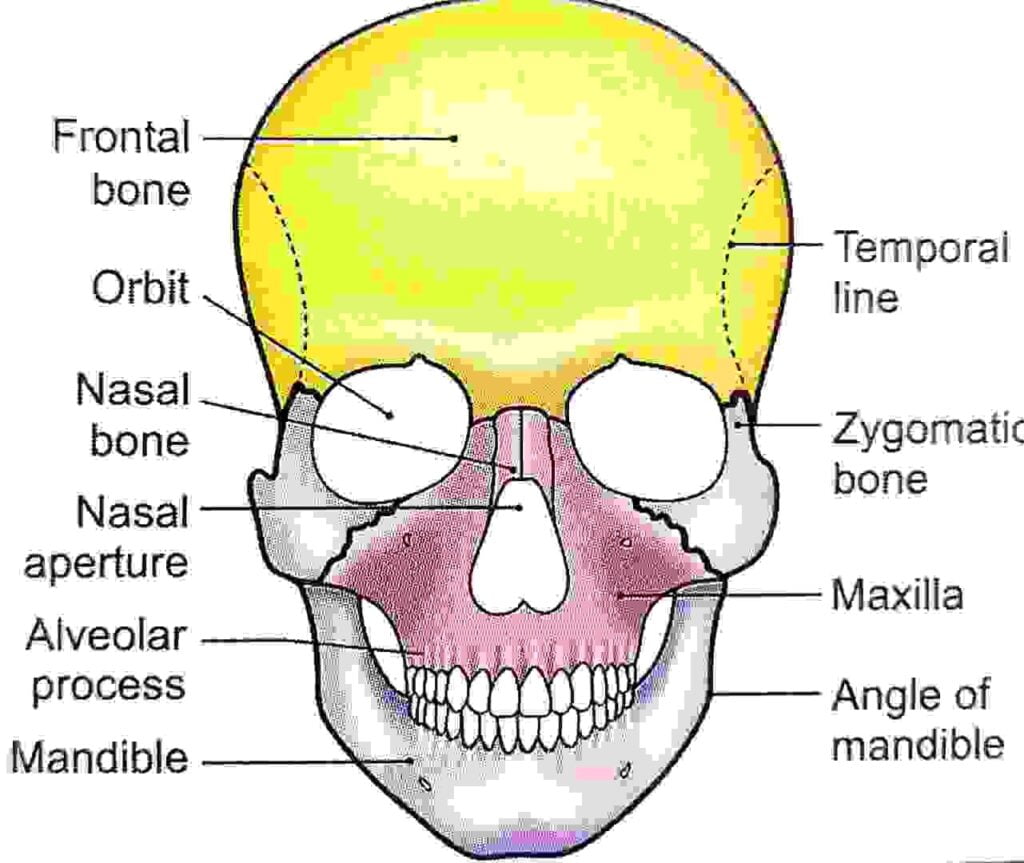
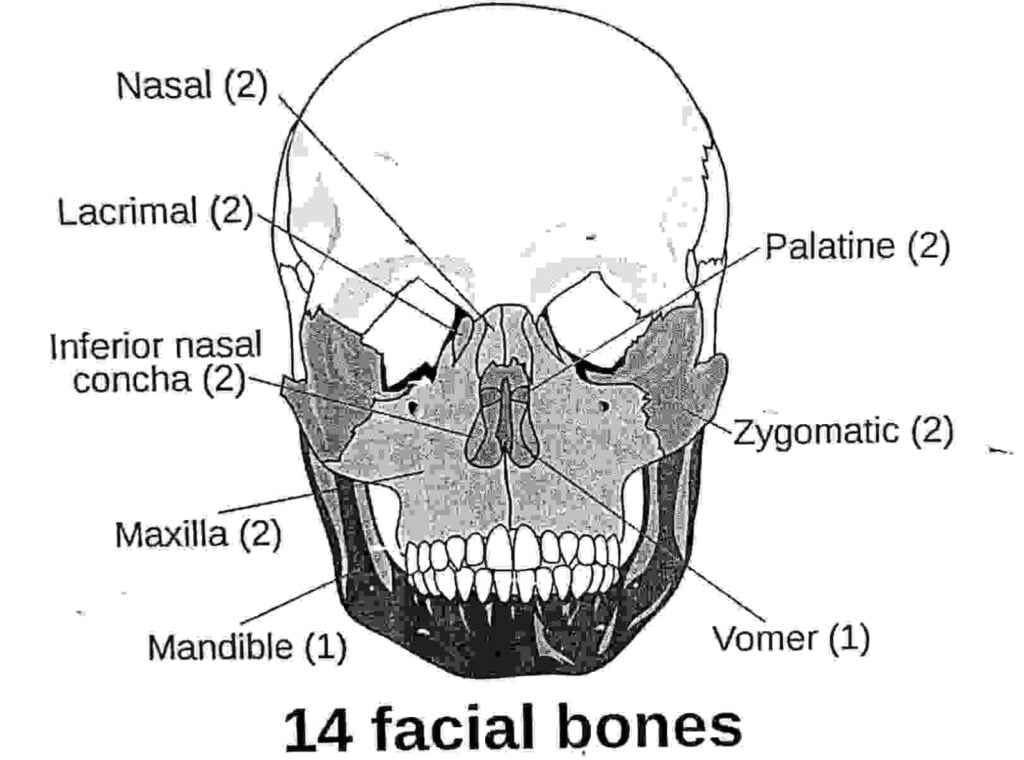
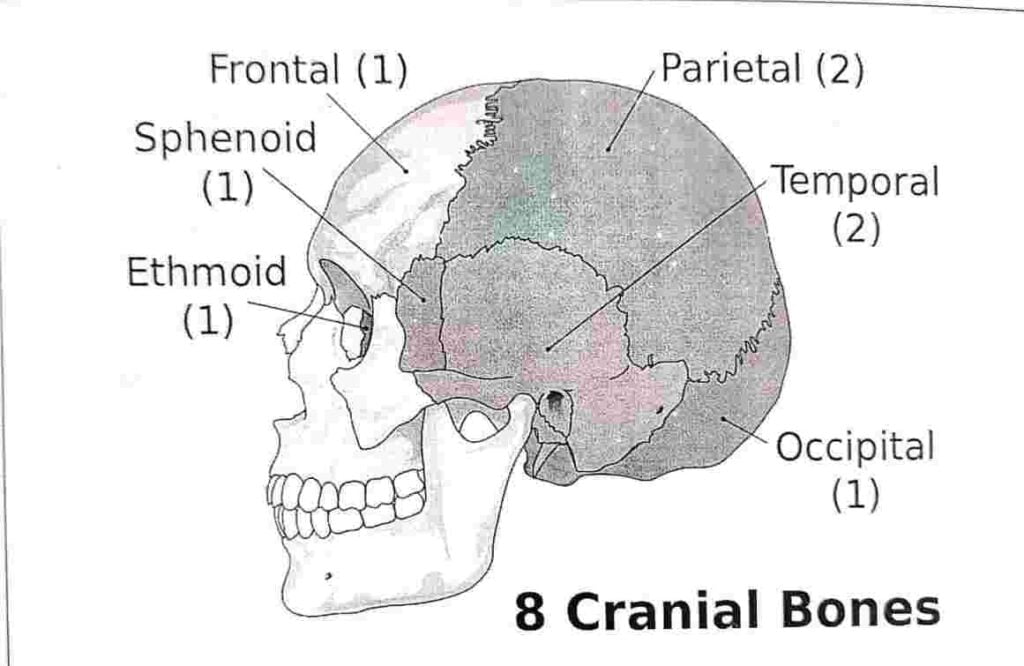
Skull bone= 28
| Cranium bone =14 | | facial bone = 14 | |
| Paired | Unpaired | Paired | Unpaired |
| I. Parietal | I. Frontal | I. Maxilla | I. Mandible |
| II. Temporal | II. Occipital | II. Zygomatic | II. Vomer |
| III. Malleus | III. Sphenoid | III. Nasal | |
| IV. Incus | IV. Ethemoid | IV. Lacrimal | |
| V. stapes | | V. Palatine
VI. Inferior nasal concha | |
Vertebrae = 33 [ after fusion 26]
| I. Cervical = 07 | |
| II. Thoracic = 12 | |
| III. Lumber = 05 | |
| IV. Sacral = 05 |
All fused together and become one sacrum |
| V. Coccygeal = 04 | All fused together and become one coccyx |
| |
Ribs = 24
| I. True ribs | 07 PAIR |
| II. False ribs | 03 PAIR |
| III. Floating ribs | 02 PAIR |
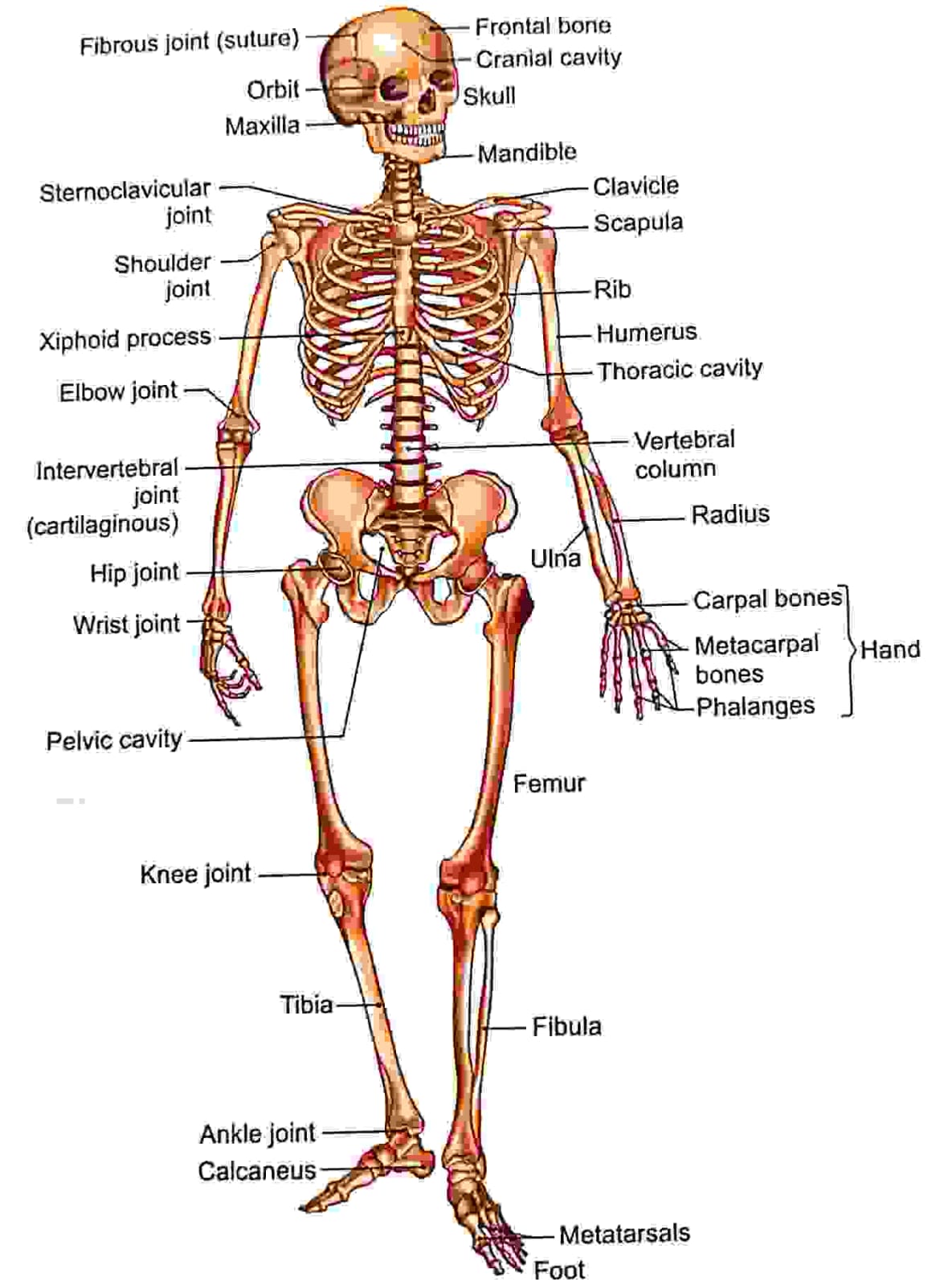
Upper limb = 64
| I. Clavicle | 01 Pair |
| II. Scapula | 01 Pair |
| III. Humerus | 01 Pair |
| IV. Ulna ( medially) | 01 Pair |
| V. Radius ( Laterally) | 01 Pair |
| VI. Carpals | 08 Pair |
| VII. Metacarpal | 05 Pair |
| VIII. Phalanges | 14 Pair |
Carpals = 08 pair
| I. proximal row | Scaphoid, lunate , triquetral, pisiform |
| II. Distal row | Trapezium, trapezoid, capitates, hamate |
Phalanges = 14 pair
| I. Thumb | Proximal , distal |
| II. Rest fingers | Proximal, middle, distal |
Lower limb = 62
| I. Hip bone | 01 Pair |
| II. Femur | 01 Pair |
| III. Ptella | 01 Pair |
| IV. Tibia | 01 Pair |
| V. Fibula | 01 Pair |
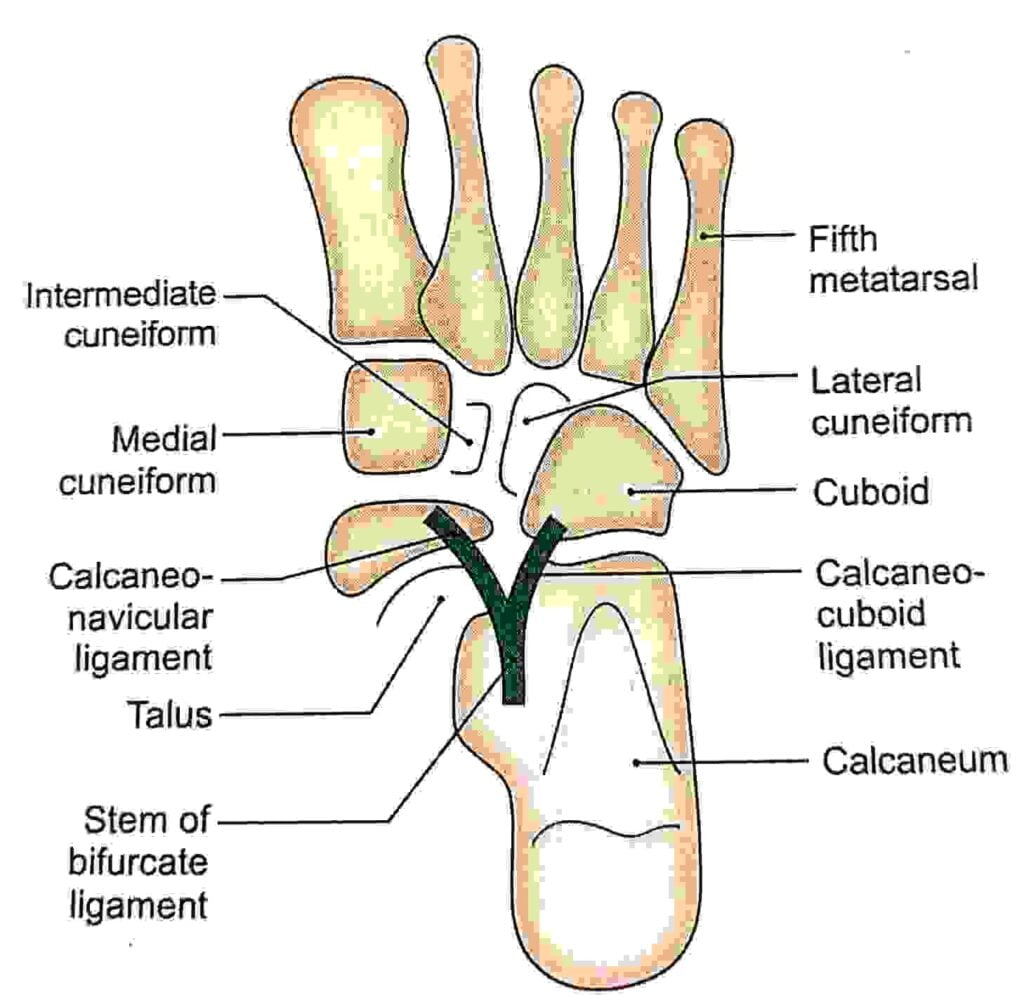
| VI. Tarsal | 07 Pair |
| VII. Meta tarsal | 05 |
| VIII. Phalanges | 14 |
Phalanges = 14 pair
| I. Toes | proximal , calcaneus |
| II. Rest toes | Proximal , middle, distal |
Pictures
introduction of bone ,introduction of bone , introduction of bone , introduction of bone





Is a bone a tissue?
Bone is living tissue that makes the body’s skeleton
Why are bones so important?
Because Bone is a hard part of the body that provide dynamic structure frame to the body.