General consideration
Table of Contents
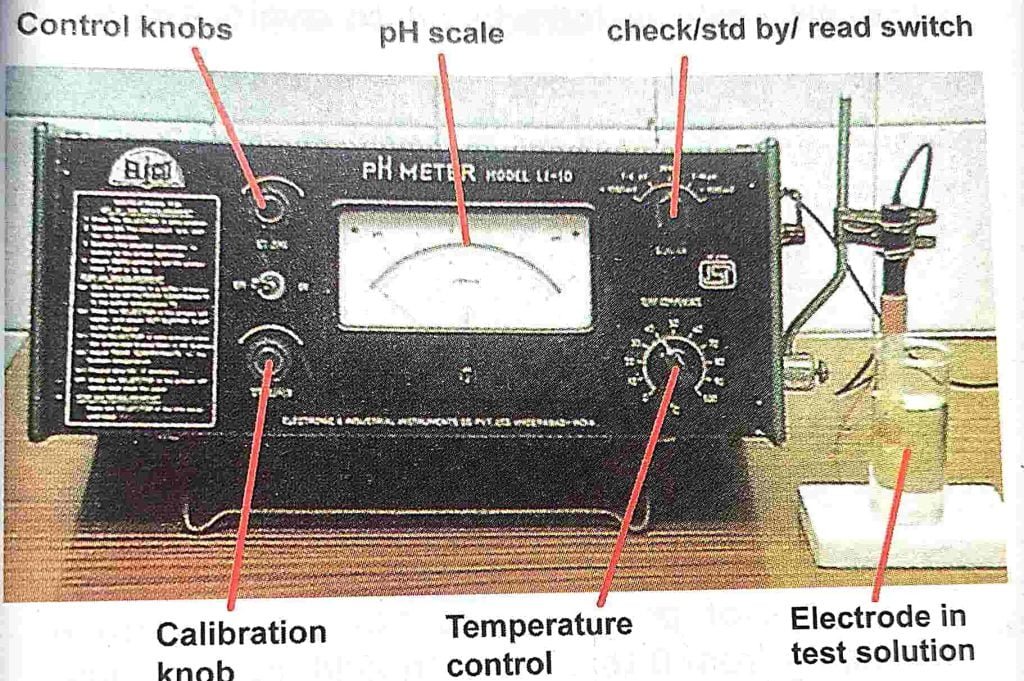
- The hydrogen ion concentration or pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is expressed as follows
- PH=1/log10(H+) =-log of hydrogen ion concentration.
- (H+) is the hydrogen ion concentration of the solution in moles per liter.
- At a given temperature, in an aqueous solution, the product of hydrogen ion concentration and hydroxyl ion concentration is constant.
- Hence, a measure of hydrogen ion concentration gives a measure of hydroxyl ion concentration.
- At a temperature of 22°C, this product conveniently happens to be exactly 10-14 (expressed in gram- molecules per liter.
- The pH scale is introduced to avoid awkward small numbers.
- The pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration, in an aqueous solution.
- If a solution is described as pH 6, its hydrogen ion concentration is 10-6 and its hydroxyl ion concentration is 10-8 at room temperature.
- The value of using pH can be seen in the case of human blood which has an extremely low hydrogen ion concentration. Blood H+ 0.398 x 10-7
- Blood pH log (0.398 x 10-7) = 7.4
- The scale of the pH meter is normally taken as extending from 0 to 14 pH.
- An acid solution has a pH value less than 7.0 and a basic solution has a PH value greater than 7.0 A neutral solution has a pH value of 7.0.
- A change of one pH meter unit corresponds to a 10-fold change in the hydrogen ion concentration of the solution.
- The most reliable and convenient method for measuring pH is by the use of a pH meter.
- It measures the e.m.f. of a concentration cell formed from a reference electrode, the test solution and a glass electrode, expressed diagrammatically as follows:
- Ag.Agcl
- (0.1M) Hcl/glass
- Test solution
- KCl( saturated)
- Hg2cl2
principle of pH meter
- When the pair of electrodes or a combined electrode (glass electrode and calomel electrode) is dipped in an aqueous solution, a potential is developed across the thin glass of the bulb (of glass electrode).
- The electromotive force (e.m.f.) of the complete cell (E) formed by the linking of these two electrodes at a given solution temperature is therefore –
- E = Eref – Eglass
- Eref is the potential of the stable calomel ref electrode, which at normal room temperature (25°C ± 5°C) is + 0.250V.
- Eglass is the potential of the glass electrode which depends on the pH of the solution under test.
- The resultant small e.m.f. can be recorded potentiometrically by using a vacuum tube amplifier.
- Variations of pH with E may be recorded directly on the potentiometer scale graduated to read pH directly.
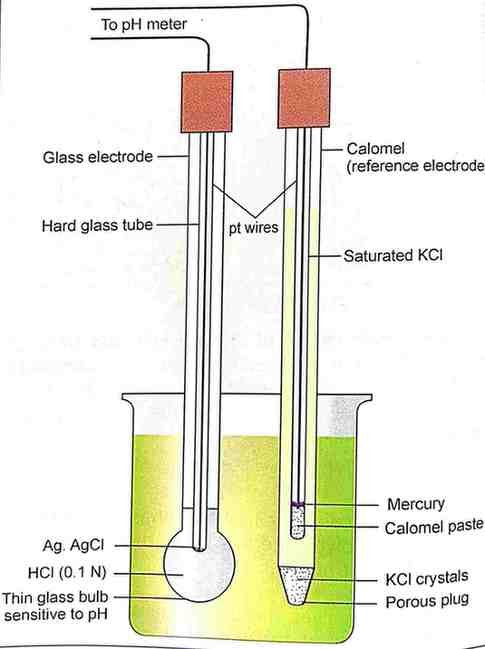
Important components of a pH meter
- glass electrode
- calomel electrode
Glass electrode
It consists of a very thin bulb about 0. 1 mm thick blown onto a hard glass tube of high resistance.
The bulb contains 0. 1 mol/liter HCL connected to a platinum wire via a silver-silver chloride combination.
Calomel electrode
It consist of a glass tube containing saturated KCL connected to platinum wires through mercury mercurous chloride paste.
What is a pH Meter used for?
A pH meter is an instrument used to measure hydrogen ion activity in solutions