prothrombin time procedure
- INTRODUCTION
- PRINCIPLE
- METHOD
- SPECIMEN
- NORMAL RANGE
- REQUIREMENT
- PROCEDURE
- CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
- NOTES
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION of prothrombin time
- Prothrombin time (PT) is a blood test that measures the time it takes for the liquid portion (plasma) of your blood to clot.
- It measures the function of a part of the clotting system
PRINCIPLE
- Prothrombin time test determines the clot- ting time of plasma in the presence of an optimal concentration of thromboplastin (prepared from human or rabbit brain) and indicates the efficiency of the extrinsic clotting system.
- Thrombokinase preparation containing calcium ions is added to citrated plasma of patient’s blood. In the presence of factor VII, stage 2 of coagulation mechanism is triggered and the clotting time is recorded. Since factors XII, XI, VIII and platelets are bypassed, the test depends upon the activity of factors VII, V, X, II and I. Deficiency of any of these factors may cause prolongation of clot formation in this test
METHOD
- Quick’s method
Specimen
- Citrated plasma
Normal range
- 14 +_ 2 second
Requirement
- Water bath (37°C)
- Stop watch
- Test tubes (10 x 100 mm)
- Brain thromboplastin (or commercially available thrombokinase tablets) with assigned ISI
- 0.15 g/dl calcium chloride
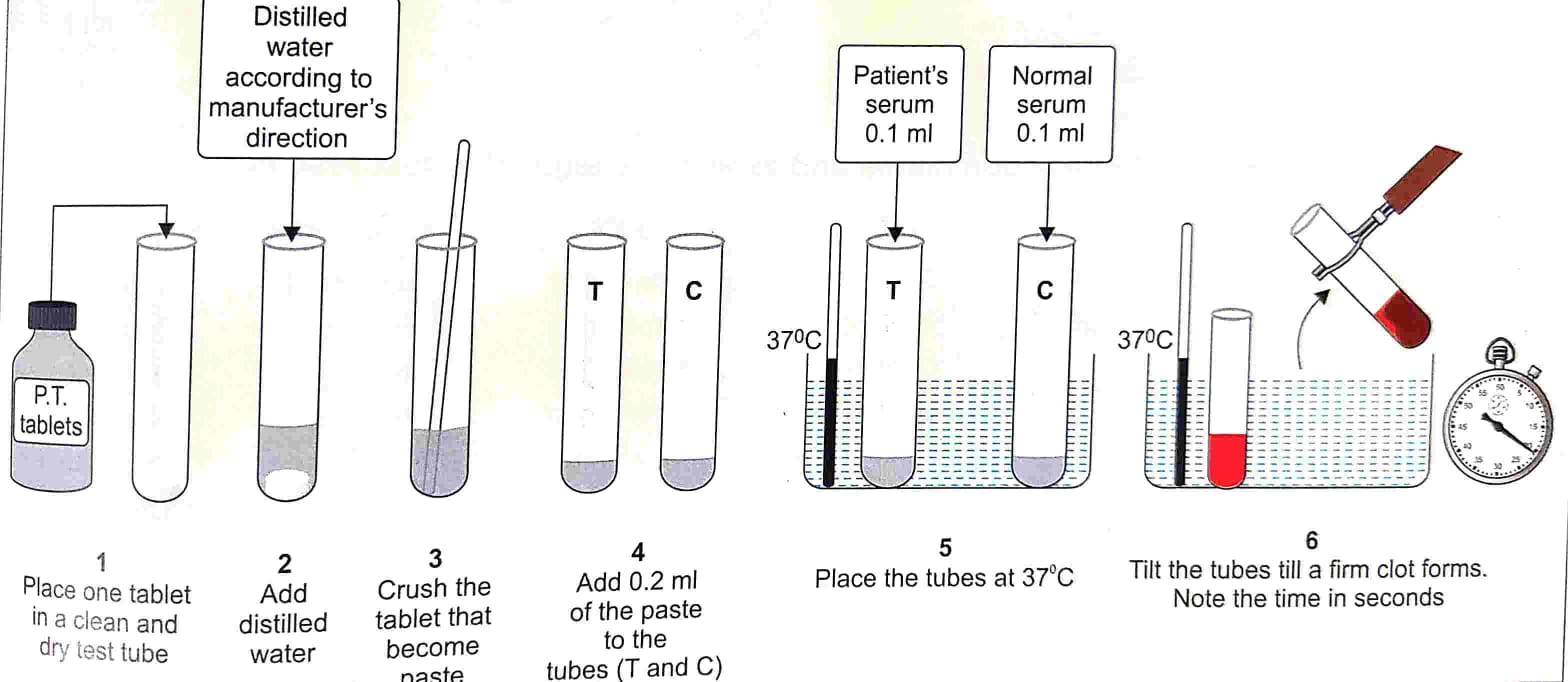
Procedure
1. Place a test tube containing about 2 ml of calcium chloride at 37°C.
2. Pipette 0.1 ml of plasma in a small test tube (10 x 100 mm).
3. Add 0.1 ml of brain thromboplastin and mix (or use thrombokinase tablets according to manufacturer’s directions).
4. Wait for 2 minutes.
5. Add 0.1 ml of pre-warmed calcium chloride solution, mix and start the stop watch.
6. Hold the tube in front of a source of light and keep tilting the tube gently. At the first appearance of a fibrin clot, stop the watch immediately.
7. Record the time.
8. Repeat the steps 1 to 7 twice to check the reliability of results.
9. Repeat the procedure by using normal plasma.
10. Note prothrombin time in seconds.
11. Report PT results as INR (Refer to the topic “Calibration and quality control” of coagulation tests for the information on ISI and INR, P 1271).
clinical significance
- The prothrombin time is the time it takes plasma to clot after addition of tissue factor (thromboplastin obtained from rabbit or human brain).
- This measures the quality of the extrinsic pathway (as well as the common pathway) of coagulation. The speed of the extrinsic pathway is greatly affected by levels of factor VII in the body.
- Prothrombin (factor II) is synthesized in the liver in the presence of vitamin K. Factor VII is also synthesized in the liver, which is related to prothrombin. In clotting mechanism in stage 2, pro- thrombin is converted to thrombin, which transforms soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin clot. Abnormal prothrombin time suggests stage 2 defect. Prolonged prothrombin time is related to the deficiencies of factors II, V, VII, and X. Since excess of coumarin group drugs may lead to hemorrhagic conditions, prothrombin time determination is also used to monitor the drug therapy. PT test is used in conjunction with the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) which measures the intrinsic pathway.
note:-
- INR =(PT test/PT normal)ISI
- If PT test=14 seconds and PT of normal control=12 seconds,and ISI of ” test thromboplastin=1.6 INR=(14/12)1.6=1.85
- Normal range of INR for a healthy persons is 0.9- 1.3.
- For patients on warfarin therapy, INR values range from 2.0-3.0.
- A high INR level (i. e. INR > 5 indicates that there is a high chance of bleeding. Similarly, if the INR <<0.5 indicates that there is a high chance of having a clot.
- The test reagent (brain thromboplastin) can be prepared in the hospital laboratory.
- If manufacturer’s reagents are used it is necessary to follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Generally manufacturers supply (a) Tablet.: It is crushed and mixed with few drops of distilled water to get homogeneous paste. It contains thromboplastin and calcium chloride (b) Powder: It is dissolved with the diluent (about 2.5 ml) to get homogeneous suspension.
- 0.2 ml preincubated suspension (at 37°C) is mixed with 0.1 ml of plasma and formation of fibrin clot is observed.